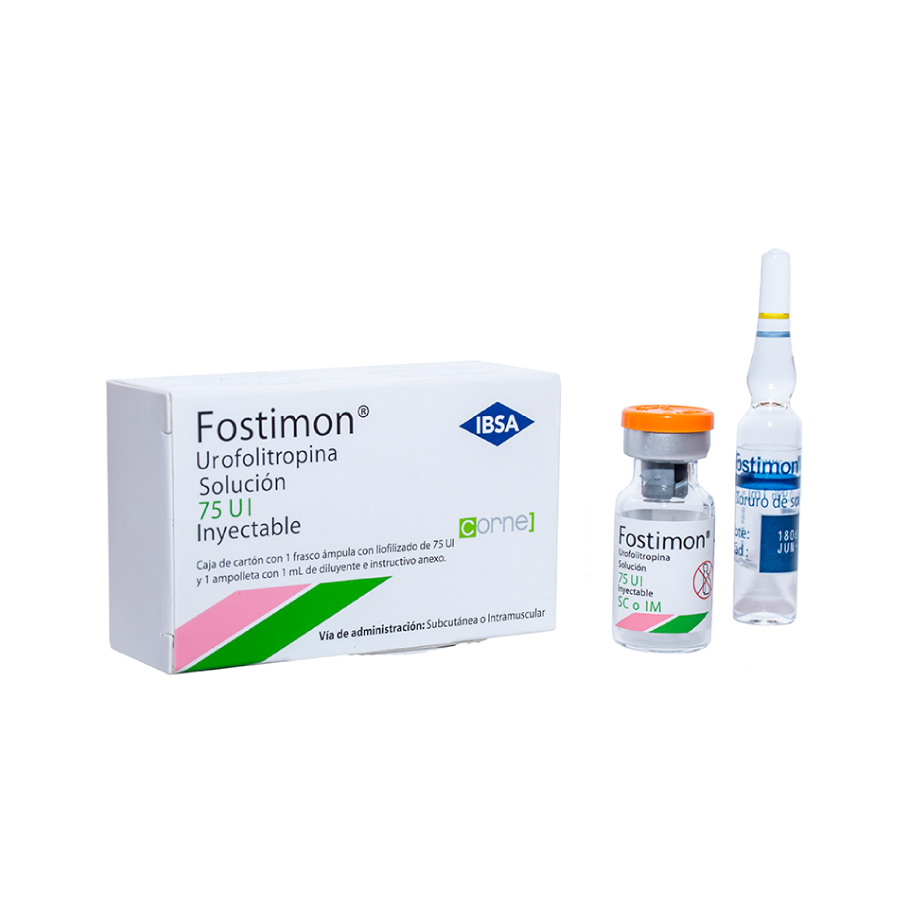
What Fostimon Is And What It Is Used For
- Fostimon is used to induce ovulation in women who are not ovulating and who have not responded to any other drug treatment (clomiphene citrate).
- Fostimon is used to develop more follicles (egg vesicles), and thus more eggs, in women undergoing assisted reproduction.
The active substance urofollitropin is a very pure human follicle-stimulating hormone ( FSH ) that belongs to a group of medicines called gonadotropins.
Fostimon should only be used under a doctor’s supervision.
What You Need To Know Before Using Fostimon
Before starting treatment, your and your partner’s fertility should be evaluated.
Do Not Use Fostimon If You Have Any Of The Following Conditions:
- Enlargement of the ovaries or ovarian cysts not caused by a hormonal disorder ( polycystic ovary syndrome )
- Gynecological bleeding, where the cause is unknown
- Malignant tumor of the ovaries, uterus, or breasts
- Abnormal swelling ( tumor ) in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus (brain)
- If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to urofollitropin or any of the other ingredients of Fostimon.
Fostimon should not be used during early menopause (when a woman’s menstruation ceases), genital malformations, or muscle knots ( fibroids ) in the uterus that would make a normal pregnancy impossible.
Take Special Care With Fostimon:
No allergic reactions have been reported with Fostimon, tell your doctor if you have had any allergic reactions to similar medicines.
Treatment increases the risk of developing a condition called ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) (see section Possible side effects ). If hyperstimulation of the ovaries occurs, treatment should be discontinued and pregnancy avoided.
The first signs of ovarian hyperstimulation are a pain in the lower abdomen as well as nausea, vomiting, and weight gain. If these symptoms occur, contact your doctor as soon as possible. In severe but rare cases of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, the ovaries may become enlarged and fluid may accumulate in the abdomen or thoracic cavity.
The drug used to achieve the final release of fully developed eggs (which contains human chorionic gonadotropin – hCG ) may increase the likelihood of OHSS. It is therefore not advisable to be treated with hCG where OHSS has developed and you should not have intercourse, even if you use a barrier contraceptive method for at least 4 days.
It should be noted that miscarriages are more common in women with fertility problems than in the rest of the population.
In patients undergoing ovulation stimulation, the incidence of multiple births or multiple births increases compared with natural conception but can be minimized by using the recommended dose.
Women with damaged fallopian tubes have a slightly increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Multiple births and characteristics of parents undergoing fertility treatment (eg mother’s age, sperm quality) can be associated with an increased risk of congenital malformations.
Treatment with Fostimon can, just like the pregnancy itself, increase the risk of getting a blood clot. Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel, usually in the veins of the legs or lungs.
Discuss this with your doctor before starting treatment, especially:
- If you already know that you have an increased risk of getting a blood clot
- If you, or anyone else in your immediate family, has had a thrombosis
- If you are severely overweight.
This medicine is made from human urine. The risk of transmission of infectious substances, which can cause infection or disease, can not be completely ruled out. This risk is limited by the use of manufacturing methods that include the removal of viruses, in particular HIV, herpes virus, and papillomavirus.
No cases of viral infection have been reported following treatment with Fostimon.
Other Medicines And Fostimon
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
Fostimon should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Fostimon Injection How To Use
Dosage and duration of treatment:
Always use Fostimon exactly as your doctor has told you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
Women who do not ovulate and have irregular periods or do not menstruate:
If you are menstruating, treatment should be started within the first 7 days after menstruation begins (the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle).
You get a Fostimon injection every day, either under the skin ( subcutaneously ) or in a muscle ( intramuscularly ).
The usual starting dose is 75-150 IU FSH (Fostimon) every day. If necessary, this dose can be increased by 37.5-75 IU at 7 or preferably 14-day intervals to achieve the appropriate treatment response.
The maximum daily dose is usually not higher than 225 IU.
If the doctor does not see any effect after 4 weeks of treatment, the treatment cycle will be interrupted. In the next cycle, your doctor will prescribe a treatment with a higher starting dose than in the previous cycle.
To induce final follicular maturation when the sufficient effect is achieved (sufficient growth of the follicles), an injection of another drug (containing hormone et hCG ) is given. This happens 24-48 hours after the last Fostimon injection. You are recommended to have sexual intercourse on the day of hCG – injection a given and even the next day.
If the effect becomes too strong, treatment should be discontinued and hCG will not be given (see Fostimon side effects ). In the next cycle, your doctor will prescribe a dose that is lower than the one in the previous cycle.
Women undergoing ovarian stimulation for multiple follicle development before in vitro fertilization or other assisted reproduction techniques:
Option 1 If you are menstruating:
Treatment should be started 2 or 3 days after the start of menstruation (days 2 to 3 of the menstrual cycle).
Dose a given as a subcutaneous or intramuscular injection every day.
The usual dose for overstimulation of the ovaries is 150-225 IU Fostimon every day. The treatment continues with a dose that is adapted to your individual needs until appropriate follicle development has been achieved. This is achieved on average on the tenth day of treatment (may vary from 5-20 days) and checked with blood tests and/or ultrasound examination.
The maximum daily dose is usually 450 IU.
When satisfactory follicular maturation has been achieved, an injection of another drug is given to induce final follicular maturation. Fostimon contains up to 10,000 IU of human chorionic gonadotropin ( hCG ). It is given 24-48 hours after the last Fostimon injection.
Egg cells will be collected about 35 hours later.
Option 2. When using a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist ( GnRH – agonist ):
Fostimon is given approximately 2 weeks after treatment with GnRH – agonist one started. Both treatments continue until appropriate follicular development is achieved. Fostimon uses is given as a subcutaneous or intramuscular injection every day.
Example: After 2 weeks of treatment with GnRH agonist, 150-225 IU Fostimon can be given for the following 7 days. Then dose one is adjusted according to the response from the ovaries.
How to give Fostimon:
Fostimon is given as a slow subcutaneous (under the skin) or intramuscular (in a muscle) injection. Each bottle is for single use only and the solution should be given immediately after reconstitution.
After appropriate training, your doctor may ask you to inject Fostimon yourself.
Then the doctor must first:
- Let your practice how to proceed to give a subcutaneous injection
- Show you suitable injection sites on the body
- Show how to prepare the injection solution
- Be sure to show you how to make the right dose of the injection solution
In addition to ampoules, other forms of medicine should be considered when self-administering patients.
Carefully read the following instructions before injecting Fostimon yourself:
Preparation and injection of 1 bottle of Fostimon, using 1 powder bottle:
Injection one should be prepared just before you are ready to take it, use the liquid in ampoule one (the solvent, which is 0.9% sodium chloride in water for injections) contained in each pack.
Prepare a clean work surface and wash your hands. The hands and tools you use must be as clean as possible.
Place the following equipment on the work surface:
- 2 alcohol wipes (cotton swabs or compresses with alcohol) (not included in the package)
- 1 vial of Fostimon powder
- 1 ampoule with diluent
- 1 syringe (not included in the package)
- 1 injection needle for the preparation of solution for injection one (not included in the package)
- 1 thin injection needle for subcutaneous injection (not included in the package)